The OmicsBox Genome Analysis Module allows executing eukaryotic de-novo and RNA-seq based gene finding with Augustus. In this way, it is possible to discover novel, putative coding genes and their genomic positions for yet uncharacterized genome. Based on the Augustus algorithm an ‘ab-initio’ (DNA sequences only), as well as RNA-seq guided (BAM files) gene predictions, are supported. We will show below that the RNA-seq guided strategy increases prediction accuracy significantly.
How to increase prediction accuracy with a RNA-seq guided strategy
In this evaluation, we will guide you through a typical gene finding process while comparing the different results obtained using the ‘ab-initio’ and the RNA-seq supported approach. The performance (time) is also compared with the standalone Augustus version.
Used dataset
To evaluate the performance and accuracy of the gene finding features now available in OmicsBox we choose as test dataset the Chr.1 of Sus scrofa (pig) from the RefSeq database (NCBI). This dataset contains 692 contigs with a total size of 315,321 kb. Additionally, a mapped RNA-seq dataset obtained with Illumina HiSeq 2500 paired-ends from the SRA NCBI’s database (SRR3159988) was used to improve the accuracy via intron hints.
Download:
Analysis steps
To perform the gene finding, we chose the ‘Eukaryotic GeneFinding’ option and select the file which contains the uncompressed Fasta sequences. Since pigs belong to the ‘Chordata’ phylum and the ‘Mammalia’ class. We select Homo sapiens as closest species. We also activate the ‘in-frame’ stop codons, to allow the discovery of gene structures masked by a stop codon.
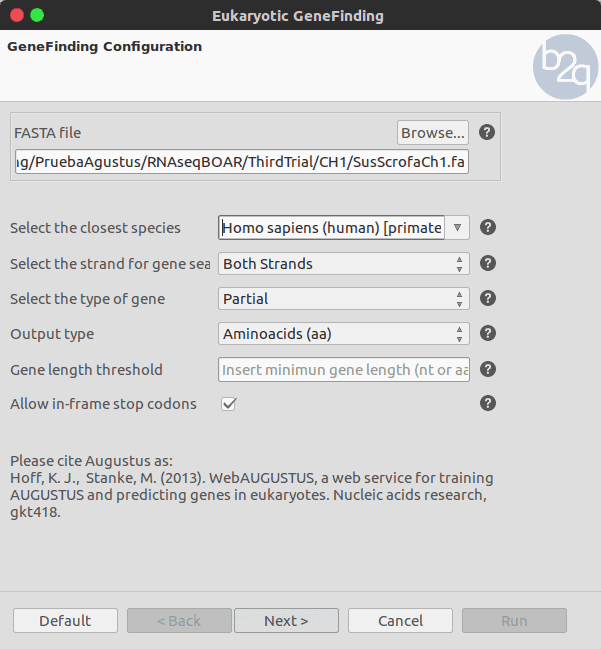
Available list of the precomputed organism in Augustus: To obtain optimal results the closest species to the one under study has to be selected. The list contains 81 different species distributed as follows:
| Kingdom | Phylum | Nº of species |
|---|---|---|
| Alveolata | Apicomplexa | 2 |
| Ciliophora | 1 | |
| Euglena | Kinetoplasmida | 1 |
| Funghi | Ascomycota | 28 |
| Basidiomycota | 11 | |
| Entomophthoromycota | 1 | |
| Microsporidia | 1 | |
| Mucorales | 1 |
| Kingdom | Phylum | Nº of species |
|---|---|---|
| Metazoa | Arthropoda | 14 |
| Chordata | 6 | |
| Nematoda | 4 | |
| Platyhelminthes | 1 | |
| Porifera | 1 | |
| Plantae | Chlorophyta | 3 |
| Magnoliophyta | 1 | |
| Streptophyta | 5 |
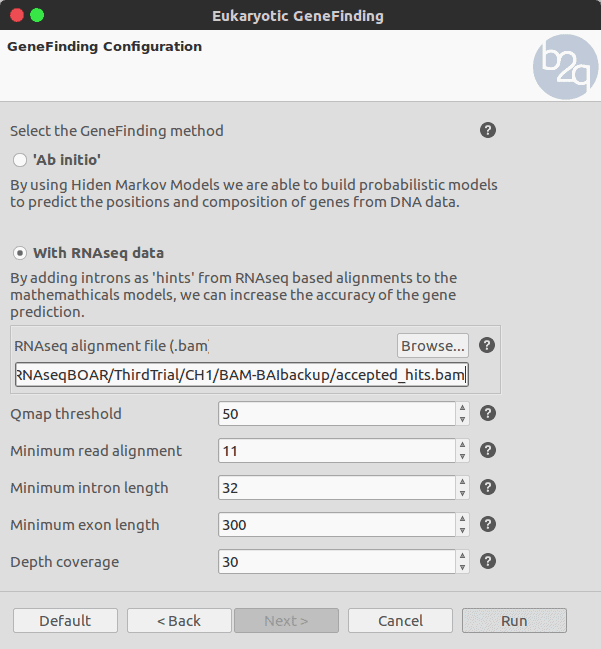
To use intron hints for the gene prediction a .bam file containing the mapped reads has to be selected. The parameters related to the RNA-seq alignment depend on the technology and the mapping algorithm (e.g. Tophat, etc.) . The rest of the parameters are set to default for this example.
The Bam file allows retrieving the genomic coordinates corresponding to the intron and exon positions. These positions are extracted and will be used as hints to support or penalise the predicted gene structures.
Benchmarks
Two benchmarks have been created to evaluate the accuracy as well as the performance.
Accuracy:
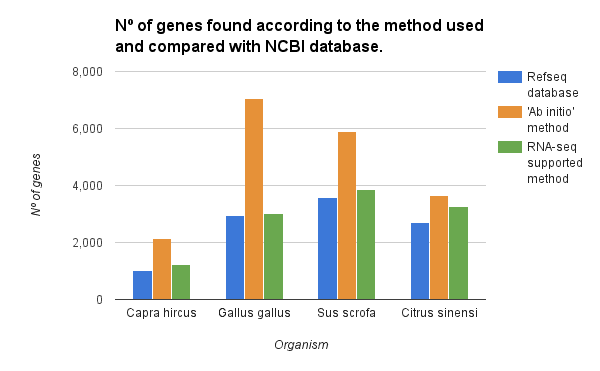
The gene finding has been performed on chromosome 1 of various species with the ‘ab initio’ and the RNA-seq supported method. For each species, we compared the number of detected genes with the genes present in the RefSeq database. As shown in the figure below both methods overestimated the number of genes. However, with the use of RNA-seq intron/exon information, we could reduce significantly the number of false positives.
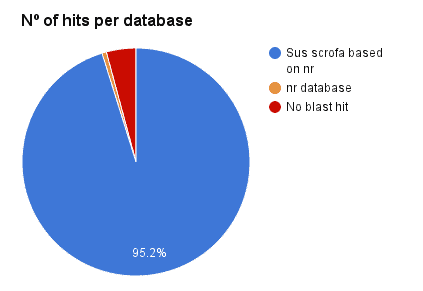
Additionally, a Blast search against ‘Sus scrofa’ (3573 genes, Chr. 1) has been performed with OmicsBox CloudBlast for all 3669 genes prediction via Augustus + RNA-Seq hits. A total of 95.2% has been confirmed (95.8% against NR). This revealed a 4.8% of false positives.
Performance:
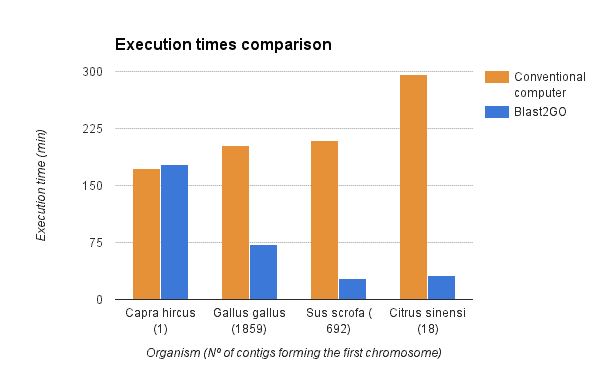
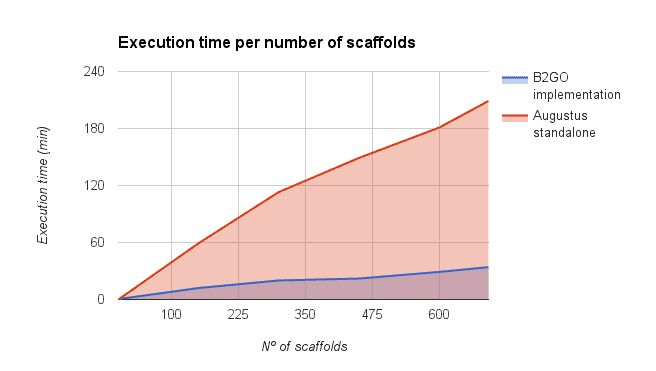
We compared the gene finding process within OmicsBox (executed via the OmcisCloud) against the local command line version of Augustus (4 2.6 Ghz cores, 16GB RAM). As shown in the figure below a parallel execution of Augustus with OmicsBox reduced the execution time drastically. However, the reduction depends on the number of scaffolds used for the predictions (more scaffolds -> more parallelized predictions -> faster).
Observations
The integration of the Augustus algorithm within OmicsBox allows performing accurate, state-of-the-art gene finding. It allows to easily reduce false positives, typically observed in ab-initio gene finding methods, via the integration of RNA-seq data. Furthermore, Blast2GO executes the predictions in a parallelized manner in a performant cloud system and saves time and frees local resources. The output generates a OmicsBox project (.box file) containing the predicted genes as well as a GFF object including the genomic annotations. These datasets can directly be used to proceed with a functional annotation with the Blast2GO methodology available via the Functional Analysis Module or be exported in different formats.
References:
Mario Stanke and Burkhard Morgenstern (2005), “AUGUSTUS: a web server for gene prediction in eukaryotes that allows user-defined constraints”, Nucleic Acids Research, 33, W465-W467